🌍 NISAR: A New Era in Earth Observation
1. Introduction: When Two Space Giants Joined Hands
NISAR (NASA–ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) is not just another mission. Nisar is something big and crucial. Nisar has combined to big countries in one place. After the announcement of this project everybody was talking about Nisar and how NASA and ISRO worked on it. this is a kind of mission that will contribute to earth’s surface research. Nasa and ISRO both are big space agencies and there working together was a very big thing for all of us. This project combined it combines the strengths of both agencies: NASA’s expertise in advanced radar technology and ISRO’s cost-effective and reliable space missions.


Usually, countries build satellites on their own, but here we are with two leading agencies of world working together for this satellite project. It shows that science is bigger than what we think of it, and it can unite two nations for the sake of earth. NASA and ISRO has created a mission that is bigger than national pride. This is historic.
It is a satellite that will look over our earth day and night.
2. What is NISAR?
Full Form & Meaning
NISAR stands for NASA–ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar. The name has a great meaning in it:
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): This radar is very special because this is a type of radar that can create very detailed and realistic images of Earth’s surface. This radar can work in dark or cloudy weather. normal cameras need sunlight to capture something but here we are with NISAR. It uses microwave signals and with the help of these signals it can see through clouds, forests, and even at night.
🔹 Unique Feature of NISAR
Most of the satellites that have created till today carries only one kind of radar,
but NISAR will carry two different radars:
As we know this mission is from two countries, so each country has their own special radar in this satellite
- L-band radar (from NASA) → from NASA, it Can pass through deep forests and wild vegetation.
- S-band radar (from ISRO) → from ISRO, it is very essential for monitoring crops, soil, and smaller-scale things and features.
And when these two kinds of radar come together, they will give scientists the most complete and accurate picture of Earth ever made. From two different lenses we will see a perfect picture of earth.
🔹 Why is this important?
Today we are all known that earth is not going to remain the same, it will change, and it is changing every moment.
glaciers are melting, forests are shrinking, seas are rising and we can see it. Here comes the important task for Nisar. NISAR will map these changes in real-time. Yes, you are right, that means scientists can study this data and can make information from it. and then farmers, environmentalists, and even governments can use its data to take action before it’s too late. And we all know how much this can help us.
3. Why is NISAR Important for Earth and Humanity?
Let’s go through the points that why Nisar is matters and why is more important than you think it is-
1. Monitoring Earth’s Climate & Environment
- NISAR will track changes in Earth’s surface—like melting glaciers, rising sea levels, shifting forests, and shrinking wetlands.
- This helps scientists understand global warming and climate change in real time.
- Example: If ice in the Himalayas melts faster, NISAR can detect the change early.
2. Disaster Management & Preparedness
- NISAR can detect ground movements before earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, or landslides.
- Governments can use this data to warn people earlier and save lives.
- Example: It can spot the ground slowly sinking in a flood-prone area, even before disaster strikes.
3. Food & Agriculture Security
- By studying soil moisture, crop growth, and deforestation, NISAR helps farmers and policymakers.
- It can predict droughts, crop failures, or floods, making food supply more secure.
4. Water & Natural Resources Management
- NISAR can track water resources, river changes, and groundwater levels. that than can help in the big problems like water Scarcity.
- Helps in planning water usage and preventing shortages in the future.
5. Global Collaboration for Humanity
- NISAR is a joint mission between NASA (USA) and ISRO (India).
- It symbolizes how the world can come together for a bigger cause—protecting the planet.
- Data will be shared worldwide, meaning not just India or USA, but all nations will benefit.

6. Long-Term Human Survival
- By giving us data about Earth’s health, NISAR ensures humanity makes better choices.
- Protecting forests, oceans, and atmosphere today means a safer tomorrow for future generations
4. India and the U.S.: A Shared Mission
ISRO’s Role (India)
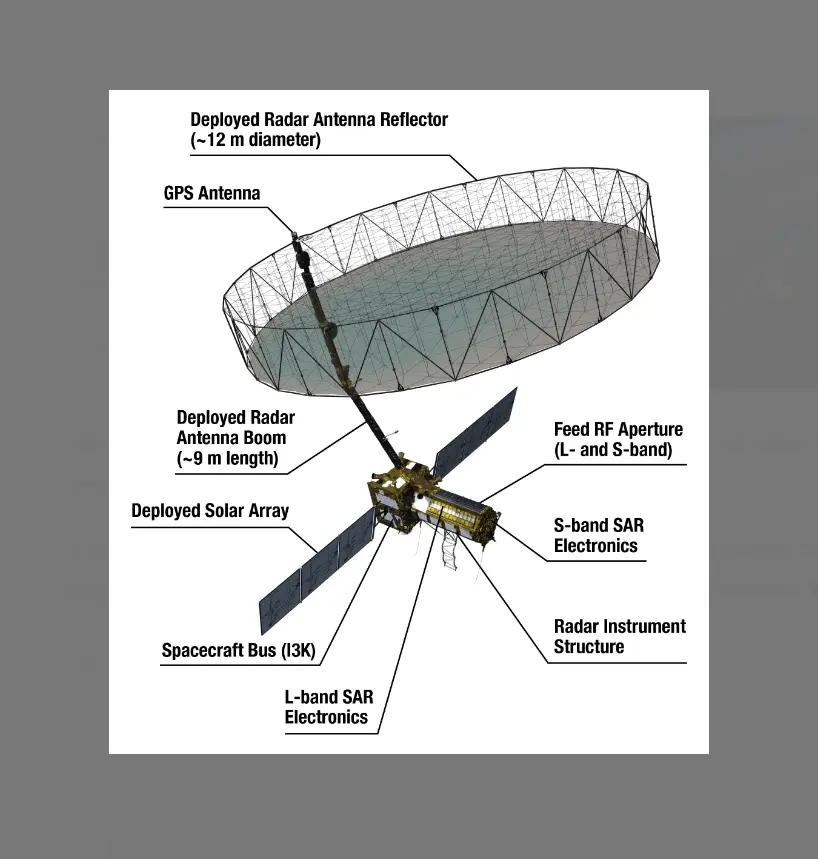
- S-Band Radar: ISRO developed the S-band radar system, which can penetrate clouds and vegetation to study land changes with great accuracy.
- Spacecraft: ISRO is responsible for building the satellite’s spacecraft bus—this is like the “body” of the satellite that carries instruments, provides power, and keeps it running.
- Launch: ISRO will launch NISAR using its powerful GSLV Mk II rocket from Sriharikota, India. This means India is literally sending the mission into space.
NASA’s Role (United States)
- L-Band Radar: NASA contributed the L-band radar, which penetrates deeper into the Earth’s surface compared to S-band. This makes it perfect for studying ice sheets, forests, and even underground shifts.
- Additional Instruments: NASA also provided essential instruments, electronics, and support systems to make sure the mission works smoothly in space.
- Data Sharing: NASA will process the data along with ISRO, making it accessible to scientists worldwide.
🔹 A Symbol of International Unity in Science
- NISAR is more than a satellite—it’s a bridge between two nations.
- At a time when the world often faces political tensions, missions like NISAR show how science can unite humanity for a common goal: protecting Earth.
- Both countries invested money, resources, and talent, proving that global challenges need global solutions.
5. Launch and Technical Details
🚀 Launch Vehicle and Site
as we all witnessed this moment and we know that NISAR was launched on July 30, 2025, at 5:40 pm IST from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre, Sriharikota. And this satellite was aboard the GSLV-F16 (Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle). And there is one more important thing in it, this was the first time that a GSLV placed a satellite directly into a Sun-Synchronous Orbit.
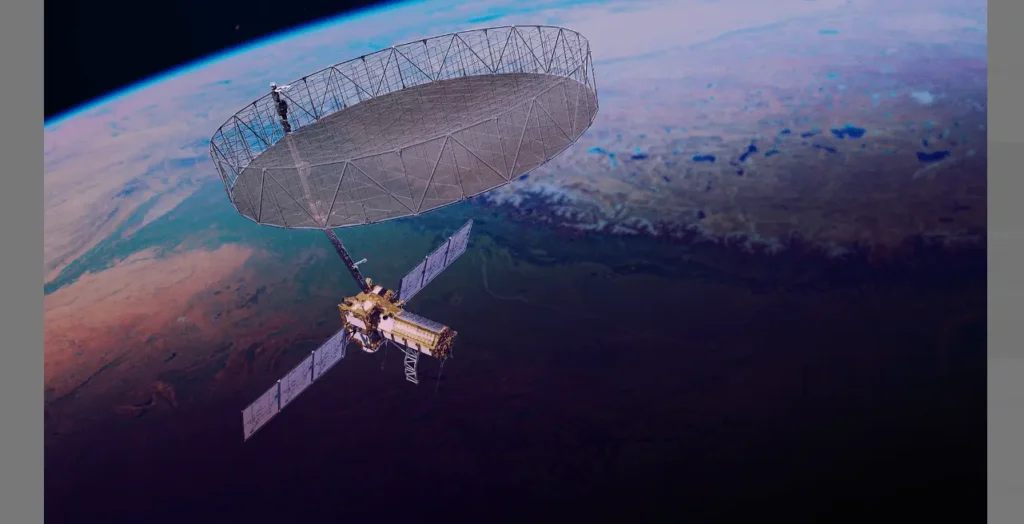
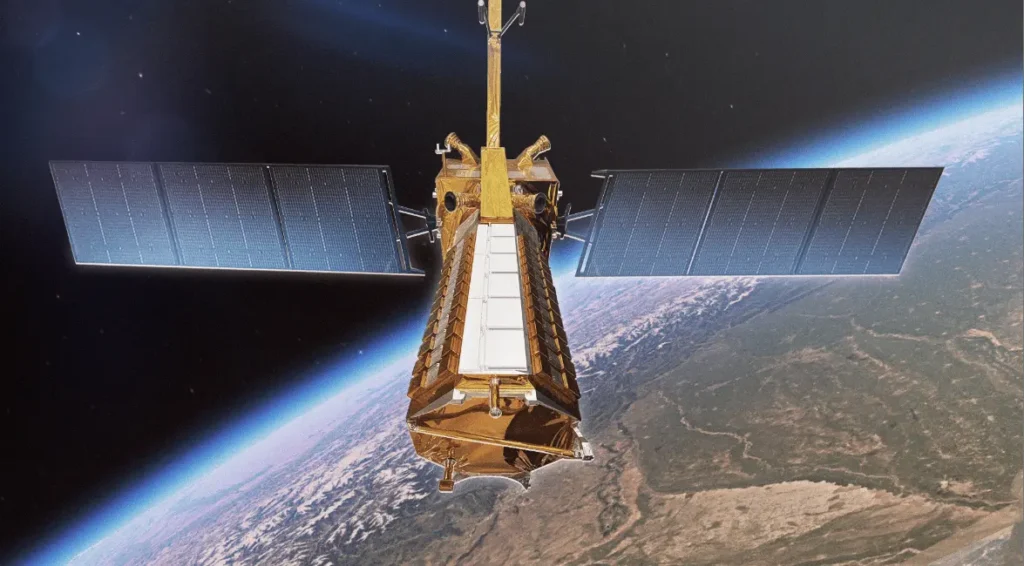


🌌 Orbit and Coverage
now the satellite is circling Earth in a 747 km Sun-Synchronous Orbit. It is completing nearly 14 orbits per day. From this vantage point, NISAR will scan the entire globe every 12 days. And this will provide the scientists data of Earth’s ecosystems, ice sheets, forests, and urban areas.
⏳ Expected Mission Life
NISAR is Designed with careful checking and modern engineering, from this NISAR carries an expected mission lifespan of at least 3 years. However, as we know many satellites that work more than their lifespan, scientists hope that NISAR too will work more than its counting years. and will continues delivering vital climate and Earth observation data.
6. The Vision Ahead
🔭 How NISAR Will Change Our Understanding of Earth
- With its dual radar systems (L-band and S-band), NISAR is already starting to reveal Earth’s silent shifts—tracking forest biomass, soil moisture, and subtle land movements that were previously hidden beneath foliage or cloud cover.
- The 39-foot deployable radar reflector successfully unfurled in orbit on August 15, 2025, a milestone that confirmed NISAR’s ability to work even more perfectly.
- Early data from the NISAR is crucial for our earth, from this data scientists can measure changes in ice sheets and glaciers, monitor subtle ground deformation that is useful for predicting landslides or earthquakes. From this data scientists can also observe ecosystem changes.
- Researchers including Michigan State University scientists are already applying NISAR data to soil moisture mapping, which could guide future agricultural decisions—from planting times to flood risk assessments.
🌱 A Step Toward Global Sustainability
- By tracking ground shifts, subsidence, melt dynamics, and water movement, NISAR provides critical data that can be used in disaster early warning systems—giving communities more time to prepare for floods, landslides, or tremors.
- Its consistent global coverage, revisiting the same spots every 12 days, ensures that even remote or cloud-covered regions—like the Himalayas or the polar ice sheets—are monitored regularly, giving scientists a baseline for climate change, glacier retreat, and sea level rise.
- The open-access nature of NISAR’s data (made available to researchers globally) means that planning for water management, agricultural resilience, and environmental conservation can be informed by reliable, up-to-date satellite information.
- Ultimately, by providing a constant, high-resolution view of Earth’s shifts—both slow and sudden—NISAR is a tool that empowers scientists, policymakers, and communities to make better decisions about how we care for the planet we share
7. Conclusion: Listening to Earth’s Heartbeat
It was a great moment When NISAR opened its giant 12-metre antenna in orbit. it was not just a technical success —it was a promise to Earth. Quietly, in its sun-synchronous orbit, it listens—day and night, rain or shine—to the subtle shifts of our planet.
NISAR as Earth’s Silent Guardian
NISAR is not just another satellite in space, it is very important for our earth. It is Earth’s silent guardian. It senses glacier melts, shifting coastlines, land subsidence, forest changes, and even the slow tectonic movements of the ground. These changes are invisible to human eyes but crucial for our future. From this, we will learn the main aspects of problems. In doing so, it protects the ecosystems and gives us time, so that we can understand the problem and can respond to it, protect what we can.
The Hope It Brings for Future Generations
For future generations, NISAR is a rope of hope. This mission embodies science, collaboration, and foresight—all in one. By providing timely data, it will give us information about earth’s surface and its resources. And then we can manage water and food resources, and plan sustainable futures. We can monitor big disasters and maybe stop them from happening. This way NISAR will play a big role for our generations. In Earths rapidly changing climate, NISAR’s voice will guide us to new paths.
In short NISAR will tell us the health of our earth so we can cure it and find right medicine for it.